Introduction
Supply Chain Risk is a major issue for businesses and consumers (think Colonial Pipeline or JB Meat Packing). Security incidents have been reported for centuries and even millennia regarding supply chain disruptions due to piracy/theft from transporting food, precious metals, goods, or the myriad other expensive products. The risk of shipwrecks from storms has also been in the limelight.
As the world has gone digital, the supply chain risks have only increased as the digital highway provides extensive information availability and enables communication and collaboration because of the technological integration of systems and processes, creating an interconnectedness at every integral part of a supply chain.
The fourth industrial revolution is also continuing to push communication and Information Technology (IT) further. Moreover, the recent technological advancement in digitalization and big data analytics require businesses to create a comprehensive and proactive Supply Chain Risk Management (SCRM) approach.
Let’s examine some supply chain risks, their impact, root causes of risks, SCRM technology, and mitigation of supply chain risks.
What Is the Impact of a Supply Chain Risk?
In addition to various other causes, the COVID-19 pandemic is currently putting high pressure on numerous global industries and that results in creating massive uncertainties in ‘supply and demand’ and disrupting supply chains across the globe.
Managing supply chain risks has become a daunting task for supply chain managers due to various factors, such as:
- Growing global competition
- Rising cost pressure
- Ever-increasing complexity
- Increasing customers’ expectations
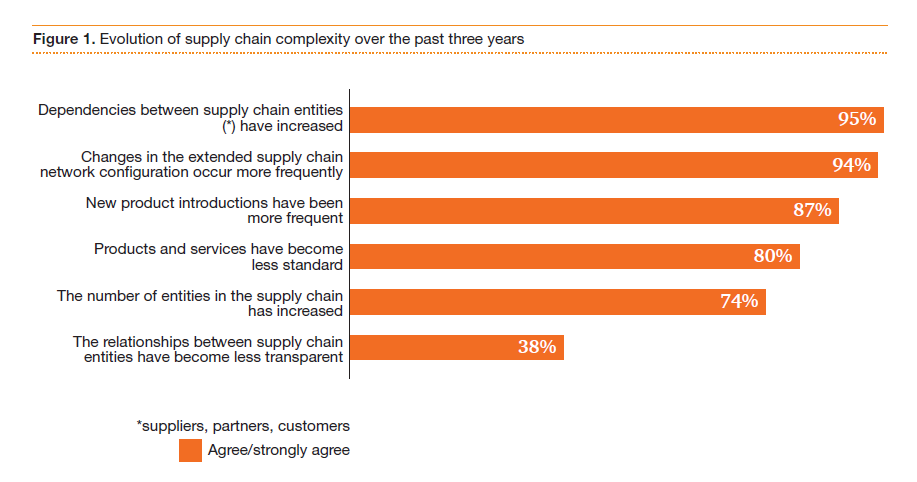
Every-increasing complexity is due to both domestic and international risks to the supply chain. The more complex a supply is, the less predictable the likelihood and the impact of disruption are. In simple words, the probability (likelihood of risk occurrence) of risks is very high under such circumstances. See the following figure for supply chain complexity drivers.

Supply chain risks and uncertainties often interrupt the operational efficiency of the supply chain and, therefore, have adverse impacts on an organization’s profits. These risks also have a bad impact on performance metrics such as inventory costs, lead-time, responsiveness, and flexibility. The risks in the supply chain may result in the inability of manufacturers to fulfill their customers’ requirements.
Why Do I Need to Discover Root Causes of a Risk?
Discovering the root causes of risk is indispensable to eliminate risk. If you successfully discover a cause of risk occurrence, you can develop an effective and long-term risk management solution. However, uncovering the root causes is not an easy task due to several reasons, such as lack of communication, missing information, and high complexity. However, you can pay heed to the following questions when finding the root causes of supply chain risks:
- What was the time of the first appearance of the problem?
- How and why was the problem noticed?
- Why did the problem not appear earlier?
- What enables the risk (e.g., any potential vulnerability) to persist?
- What dependencies (e.g., systems, resources, and processes) does the risk has to maintain itself?
If you have past and future analyses of risk in place, a common discovery and presumption are that today’s risk can develop from yesterday’s solution. Hence, addressing today’s risk may need to wait for tomorrow’s solution. The way past solutions establish a new risk may discover clues to the root causes of risks.
What Do I Need to Know About Supply Chain Risk Management (SCRM)?
Supply Chain Risk Management (SCRM) is a broad subject. However, we will analyze it at the tactical level. An SCRM is a security approach used by supply chain managers to continually detect, measure, and evaluate potential supply chain disruption caused by all varieties of supply chain risks, emanating both from outside or within the supply chain. According to Global Supply Chain and Risk Management Survey, conducted by PWC, 60% of respondents said that the performance indicators of their respective companies had dropped by 3% or more as a result of supply chain disruptions.
The purpose of SCRM is to control, manage, reduce, or eliminate potential or real risk exposure to the supply chain’s performance. In fact, a risk is a potential or actual negative impact on the supply chain performance. If a company deploys an effective risk management approach, the cost can significantly be decreased by reducing risk probability and impact of reduced performance and supply chain disruption.
What Actions Are Needed to Mitigate Supply Chain Risks?
The following section lists some remedial measures to mitigate supply chain risks.
- Create and implement a reliable Business Continuity Plan (BCP).
- Implement a dual sourcing strategy or a fault tolerance, which allows you to replace an alternative system if a primary system fails.
- Use hazard maps to evaluate geographic risks for suppliers.
- Utilize both regional and global security strategies.
- Increase safety stocks and inventory levels.
- Develop distribution centers in different regions.
- Pursue first and second tiers supplier collaboration.
- Acquire sufficient flexibility and redundancy across the value chain to absorb disruption and adapt to change.
- Ensure visibility, collaboration, and information sharing among upstream and downstream supply chain partners.
- Ensure alignment and integration among internal business functions on operational, tactical, and strategic levels.
- Manage complexity by standardizing and simplifying interfaces, networks and processes, product portfolios and product architectures, and operating models.
- To prevent IT and cyber risks, invest in hardware and software tools.
- Invest in cybersecurity training and awareness program.
References
eBooks
- Supply Chain Risk Management: Advanced Tools, Models, and Developments by Yacob Khojastech Edition, Springer Publishers
- Revisiting Supply Chain Risks by edited by Christopher S. Tang, Springer Publishers
Web Resources
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1665642314706029#:~:text=Greater%20risk%20in%20supply%20chain,impact%20on%20supply%20chain%20performance.
- https://journal.oscm-forum.org/publication/article/supply-chain-risk-governance-towards-a-conceptual-multi-level-framework-
- https://www.cisa.gov/supply-chain
- https://www.fai.gov/topics/cybersecurity-supply-chain-risk-management
- https://www2.deloitte.com/global/en/pages/risk/cyber-strategic-risk/articles/covid-19-managing-supply-chain-risk-and-disruption.html



